# 还在用Mybatis? Spring Data JPA 让你的开发效率提升数倍!
作者:Tom哥
公众号:微观技术
博客:https://offercome.cn (opens new window)
人生理念:知道的越多,不知道的越多,努力去学
Spring Boot 作为主流微服务框架,拥有成熟的社区生态。市场应用广泛,为了方便大家,整理了一个基于spring boot的常用中间件快速集成入门系列手册,涉及RPC、缓存、消息队列、分库分表、注册中心、分布式配置等常用开源组件,大概有几十篇文章,陆续会开放出来,感兴趣同学可以关注&收藏
# 简介
JPA (Java Persistence API) 是 Sun 官方提出的 Java 持久化规范。它为 Java 开发人员提供了一种对象/关联映射工具来管理 Java 应用中的关系数据。他的出现主要是为了简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合 ORM 技术,结束现在 Hibernate,TopLink,JDO 等 ORM 框架各自为营的凌乱局面。JPA 在充分吸收了现有 Hibernate,TopLink,JDO 等ORM框架的基础上发展而来的,具有易于使用,伸缩性强等优点。
Spring Data JPA 是 Spring 基于 ORM 框架、JPA 规范的基础上封装的一套 JPA 应用框架,底层使用了 Hibernate 的 JPA 技术实现,可使开发者用极简的代码即可实现对数据的访问和操作。它提供了包括增、删、改、查等在内的常用功能,易于扩展,极大提高开发效率。
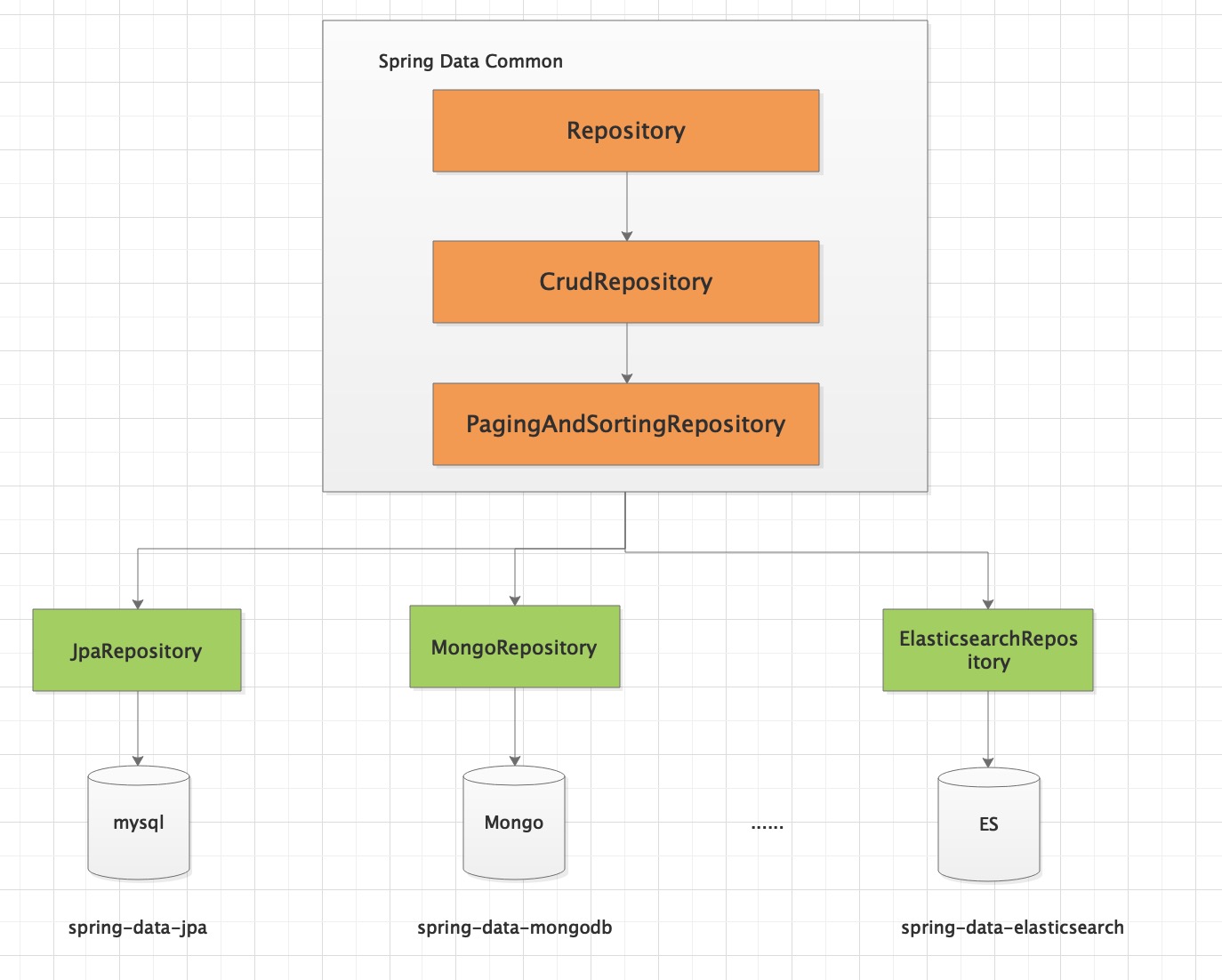
Spring Data Common 是 Spring Data 所有模块的公共部分,该项目提供了基于 Spring 的共享基础设施,它提供了基于 repository 接口以 DB 操作的一些封装,以及一个坚持在 Java 实体类上标注元数据的模型。
Spring Data 不仅对传统的数据库访问技术如 JDBC、Hibernate、JDO、TopLick、JPA、MyBatis 做了很好的支持和扩展、抽象、提供方便的操作方法,还对 MongoDb、KeyValue、Redis、LDAP、Cassandra 等非关系数据的 NoSQL 做了不同的实现版本,方便我们开发者触类旁通。
# Spring Data JPA 优势
使用广泛,大厂必备。借助于spring boot广泛受众人群,与 Spring Boot 天然集成的 Spring Data JPA 也逐渐走进了 Java 开发者的视野。JPA 可以使团队在框架约定下进行开发,几乎很难写出有性能瓶颈的 SQL。
提升开发效率。刚开始时学习语法(比如方法名、SQL 逻辑)要花点时间,一旦完成系统化的学习后。你可以熟练使用 JPA,那么半小时甚至几分钟就可以写好查询方法了;再配合测试用例,你的开发质量也会明显提高很多。
提升技术水平。Spring Data 对数据库进行了封装,统一了关系型数据库和非关系型数据的接口、公共的部分。你会发现,一旦掌握了Spring Data JPA框架后,你可以轻易实现对
Redis、MongoDB等NoSQL的操作,他们底层依赖了统一的Spring Data Common。
Spring Data和JPA的结构关系:
# 代码演示
# 外部依赖
Spring Boot 已经为 JPA 封装了starter组件,只需在 pom.xml 文件中添加jar版本依赖即可:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Spring Boot Starter Data JPA 依赖 Spring Data JPA;而 Spring Data JPA 依赖 Spring Data Commons。
# 配置文件
在配置文件 application.yaml 中配置 JPA 的相关参数,具体内容如下:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/ds0?characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 111111
# Hikari config
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
hikari:
minimum-idle: 10
maximum-pool-size: 200
idle-timeout: 60000
pool-name: MarketingHikariCP
max-lifetime: 1800000
connection-timeout: 2000
connection-test-query: select 1
jpa:
show-sql: true #在控制台打印 sql 语句
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
数据库连接用的是 JDBC,连接池用的是 HikariCP,强依赖 Hibernate;
工程结构如图所示:

# 定义实体对象
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"hibernateLazyInitializer"})
public class User {
@Id // @Id注解指明这个属性映射为数据库的主键。
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
// 名称
private String userName;
// 年龄
private Integer age;
// 地址
private String address;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
注解说明:
@Entity 是一个类注解,用来注解该类是一个实体类用来进行和数据库中的表建立关联关系,首次启动项目的时候,默认会在数据中生成一个同实体类相同名字的表(table),也可以通过注解中的 name 属性来修改表(table)名称, 如@Entity(name=“user”) , 这样数据库中表的名称则是 user 。该注解十分重要,如果没有该注解首次启动项目的时候你会发现数据库没有生成对应的表。
@Table 注解也是一个类注解,该注解可以用来修改表的名字,该注解完全可以忽略掉不用,@Entity 注解已具备该注解的功能。
@Id 类的属性注解,该注解表明该属性字段是一个主键,该属性必须具备,不可缺少。
@GeneratedValue 该注解通常和 @Id 主键注解一起使用,用来定义主键的呈现形式,该注解通常有多种使用策略,总结如下:
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY) 该注解由数据库自动生成,主键自增型,在 mysql 数据库中使用最频繁,oracle 不支持。
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO) 主键由程序控制,默认的主键生成策略,oracle 默认是序列化的方式,mysql 默认是主键自增的方式。
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.SEQUENCE) 根据底层数据库的序列来生成主键,条件是数据库支持序列,Oracle支持,Mysql不支持。
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.TABLE) 使用一个特定的数据库表格来保存主键,较少使用。
@Column 是一个类的属性注解,该注解可以定义一个字段映射到数据库属性的具体特征,比如字段长度,映射到数据库时属性的具体名字等。
@Transient 是一个属性注解,该注解标注的字段不会被映射到数据库当中。
# 数据访问层 UserRepository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
List<User> findByUserName(String userName);
List<User> findByUserNameAndAddress(String userName, String address);
// 使用 @Query查询,参数按照名称绑定
@Query("select u from User u where u.userName= :userName and u.address= :address")
List<User> queryByUserNameAndAddress(@Param("userName") String userName, @Param("address") String address);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 层次结构类图
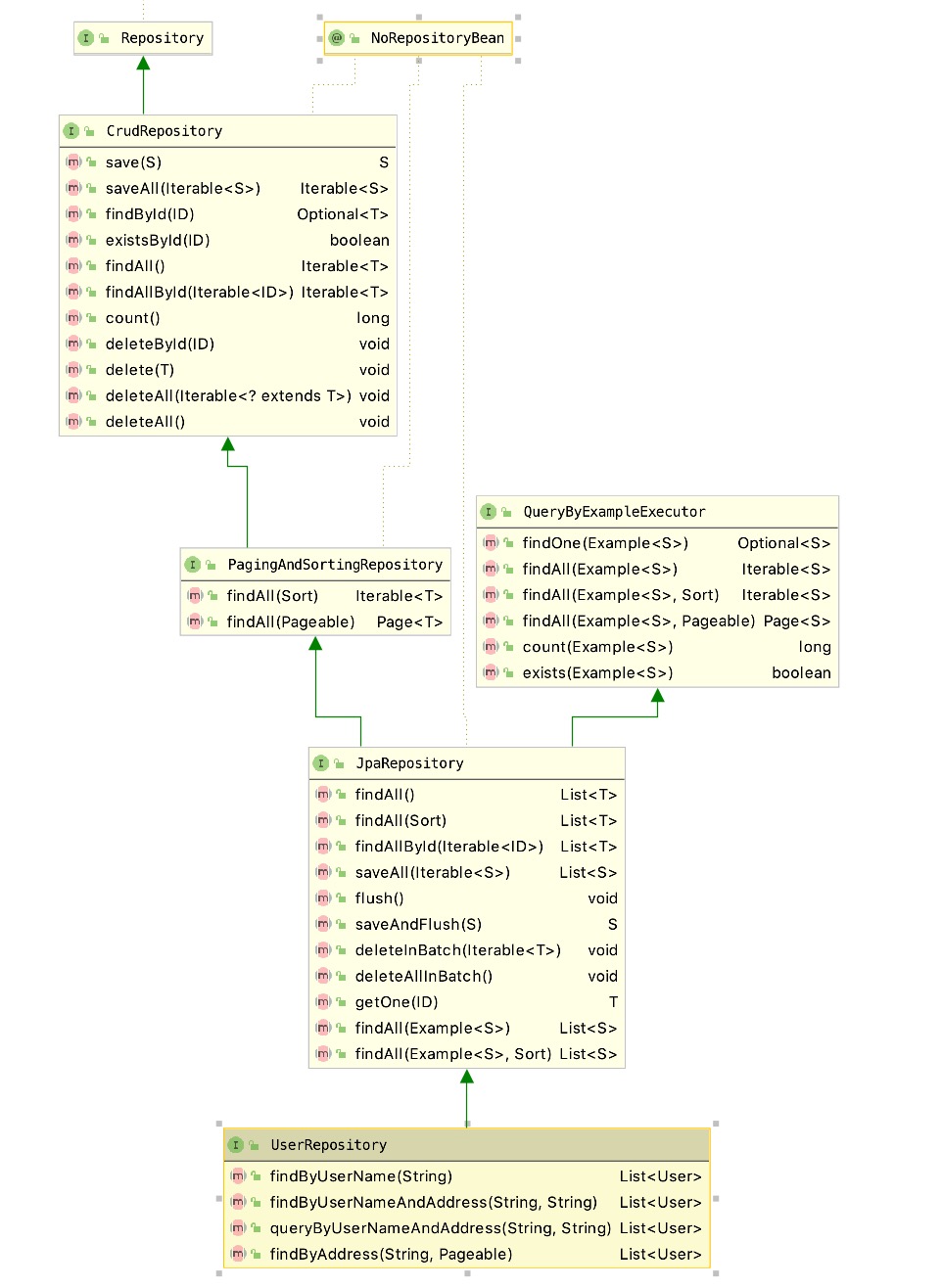
UserRepository 接口继承 JpaRepository,JpaRepository继承了接口PagingAndSortingRepository和QueryByExampleExecutor。而PagingAndSortingRepository又继承CrudRepository。
- CrudRepository: 提供了常用的存储层的增、删、改、查 操作方法
- PagingAndSortingRepository:主要用于分页查询、排序查询
- JpaRepository:上面接口是为了兼容 NoSQL 而进行的一些抽象封装。从 JpaRepository 开始是对关系型数据库进行抽象封装。JpaRepository 里面重点新增了批量删除,优化了批量删除的性能,类似于之前 SQL 的 batch 操作,并不是像上面的 deleteAll 来 for 循环删除。其中 flush() 和 saveAndFlush() 提供了手动刷新 session,把对象的值立即更新到数据库里面的机制。
除了使用继承系统提供的扩展接口类外,还可以采用约定规则方式。
自定义的简单查询就是根据方法名来自动生成SQL,具体是方法名以 findBy、existsBy、countBy、deleteBy 开头,后面跟具体的条件,举几个例子:
| 关键字 | 方法示例 | JPQL snippet |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
| Is, Equals | findByFirstname,findByFirstnameIs,findByFirstnameEquals | … where x.firstname = ?1 |
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 |
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age <= ?1 |
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 |
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 |
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 |
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 |
| IsNull, Null | findByAge(Is)Null | … where x.age is null |
| IsNotNull, NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null |
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 |
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 |
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 |
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age in ?1 |
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age not in ?1 |
| True | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true |
| False | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
Spring Data JPA 已经帮我们实现了分页,在查询的方法中,需要传入参数PageRequest,当查询中有多个参数的时候PageRequest建议做为最后一个参数传入。PageRequest是 spring 封装的分页实现类,使用的时候需要传入页数、每页条数和排序规则
@RequestMapping("/page")
public Page<User> page(@RequestParam("pageNo") int pageNo, @RequestParam("pageSize") int pageSize) {
Page<User> pageUser = userRepository.findAll(new PageRequest(pageNo, pageSize));
return pageUser;
}
2
3
4
5
Spring data 大部分的 SQL 都可以根据方法名定义的方式来实现,但是有些复杂业务场景需要使用自定义的 SQL 来查询,spring data 也是支持的。
@Query("select u from User u where u.userName= :userName and u.address= :address")
List<User> queryByUserNameAndAddress(@Param("userName") String userName, @Param("address") String address);
2
# 项目源码
https://github.com/aalansehaiyang/spring-boot-bulking
模块:spring-boot-bulking-data-jpa
2
3
