# 业务无侵入框架 Seata, 解决分布式事务
作者:Tom哥
公众号:微观技术
博客:https://offercome.cn (opens new window)
人生理念:知道的越多,不知道的越多,努力去学
Spring Boot 作为主流微服务框架,拥有成熟的社区生态。市场应用广泛,为了方便大家,整理了一个基于spring boot的常用中间件快速集成入门系列手册,涉及RPC、缓存、消息队列、分库分表、注册中心、分布式配置等常用开源组件,大概有几十篇文章,陆续会开放出来,感兴趣同学可以关注&收藏
# 简介
事务的原子性和持久性可以确保在一个事务内,更新多条数据,要么都成功,要么都失败。在一个系统内部,我们可以使用数据库事务来保证数据一致性。那如果一笔交易,涉及到跨多个系统、多个数据库的时候,用单一的数据库事务就没办法解决了。
此时需要引入分布式事务,关于分布式事务市面上有很多解决方案,之前写过一篇文章 如何解决分布式事务 (opens new window),感兴趣的同学可以看看。
本文着重讲下阿里的开源框架 -- Seata,目前在github上已经有2万 star了,非常受欢迎!!!
# Seata 框架
Seata 是一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,致力于提供高性能和简单易用的分布式事务服务。Seata 将为用户提供了 AT、TCC、SAGA 和 XA 事务模式,为用户打造一站式的分布式解决方案。
# 优点
- 对业务无侵入:即减少技术架构上的微服务化所带来的分布式事务问题对业务的侵入
- 高性能:减少分布式事务解决方案所带来的性能消耗
# AT 模式整体机制
- 一阶段:业务数据和回滚日志记录在同一个本地事务中提交,释放本地锁和连接资源。
- 二阶段:
- 提交异步化,自动异步批量清理回滚日志。
- 通过回滚日志,自动生成补偿操作,完成数据回滚。
# 核心原理
Seata 的 JDBC 数据源代理通过对业务 SQL 的解析,把业务数据在更新前后的数据镜像组织成回滚日志,利用本地事务的 ACID 特性,将业务数据的更新和回滚日志的写入在同一个本地事务中提交。
这样可以保证,任何提交的业务数据的更新一定有相应的回滚日志存在。
如果 TC 决议要全局回滚,会通知 RM 进行回滚操作,通过 XID 找到对应的回滚日志记录,通过回滚记录生成反向更新 SQL,进行更新回滚操作。
TCC 模式,不依赖于底层数据资源的事务支持:
- 一阶段 prepare 行为:调用 自定义 的 prepare 逻辑。
- 二阶段 commit 行为:调用 自定义 的 commit 逻辑。
- 二阶段 rollback 行为:调用 自定义 的 rollback 逻辑。
所谓 TCC 模式,是指支持把 自定义 的分支事务纳入到全局事务的管理中。
# Seata 流程
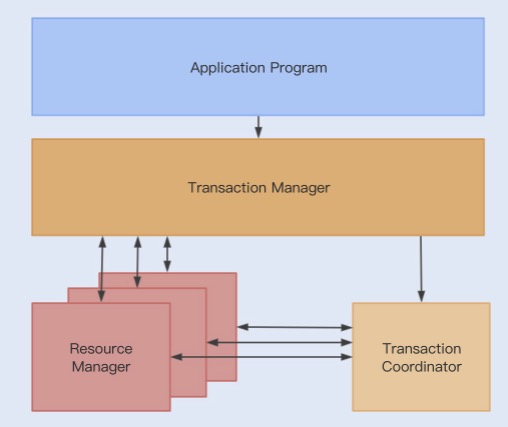
# 组成部分
事务协调器(TC):维护全局事务和分支事务的状态,驱动全局提交或回滚。
事务管理器(TM):定义全局事务的范围:开始全局事务,提交或回滚全局事务。
资源管理器(RM):管理正在处理的分支事务的资源,与TC对话以注册分支事务并报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务的提交或回滚。
# 事务流程
- TM 向 TC 申请开启一个全局事务,全局事务创建成功并生成一个全局唯一的 XID
- XID 在微服务调用链路的上下文中传播
- RM 向 TC 注册分支事务,将其纳入 XID 对应全局事务的管辖
- TM 向 TC 发起针对 XID 的全局提交或回滚决议
- TC 调度 XID 下管辖的全部分支事务完成提交或回滚请求。
# 代码演示
# 采用Docker模式,安装 Seata Server
拉取镜像:
docker pull seataio/seata-server
启动实例:
docker run --name seata-server -p 8091:8091 seataio/seata-server
# 业务场景
用户购买商品的业务逻辑。整个业务逻辑由3个微服务提供支持:
- 仓储服务:对给定的商品扣除库存。
- 订单服务:根据采购需求创建订单。
- 帐户服务:从用户帐户中扣除余额。
首先引入pom依赖,spring boot 提供了开箱即用的starter组件
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
构建了四个独立的微服务工程,系统间通过restful接口调用,满足业务需求
| 工程 | 说明 | 地址 |
|---|---|---|
| spring-boot-bulking-seata-business | 主业务入口 | http://127.0.0.1:8090/api/business/purchase/commit |
| spring-boot-bulking-seata-storage | 库存服务 | http://127.0.0.1:8083/api/storage/deduct?commodityCode=6666&count=1 |
| spring-boot-bulking-seata-order | 订单服务 | http://127.0.0.1:8082/api/order/debit?userId=101&commodityCode=6666&&count=1 |
| spring-boot-bulking-seata-account | 账户服务 | http://127.0.0.1:8081/account/debit?userId=101&orderMoney=10 |
各系统间的交互如下图所示:
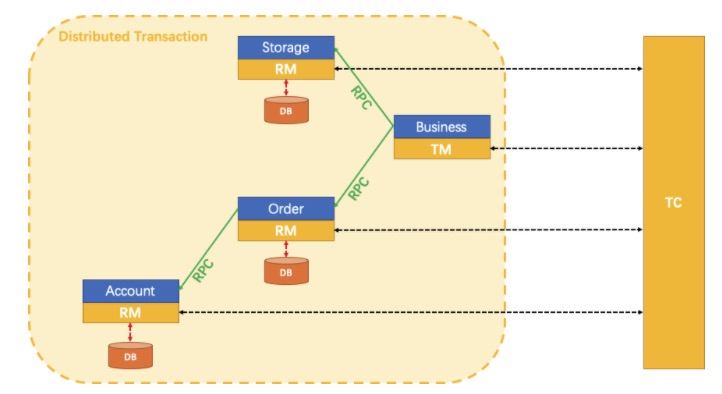
针对storage、order、account三个微服务创建3个数据库,并在不同的库中创建对应的业务表,如下:
数据库:db_seata_1
create table account (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) NOT NULL ,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0 ,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='账户表';
insert into account(id,user_id,money) value (1,"101",500);
insert into account(id,user_id,money) value (2,"102",500);
数据库:db_seata_2
create table `order`(
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) NOT NULL ,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) ,
`count` int(11) default 0,
`money` int(11) default 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='订单表' ;
数据库:db_seata_3
create table storage(
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) default null,
`count` int(11) default 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
unique key (`commodity_code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='库存表' ;
insert into storage(id,commodity_code,count) value (1,'6666',1000)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
undo_log回滚日志表,功能特殊,seata框架主要借助该表完成事务数据的回滚。
CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`xid` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`context` varchar(128) NOT NULL,
`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,
`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,
`log_created` datetime NOT NULL,
`log_modified` datetime NOT NULL,
`ext` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`,`branch_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
db_seata_1、db_seata_2、db_seata_3,每个数据库都要创建一张undo_log表。
三个工程的application.properties配置项相似,以account工程为例,内容如下:
spring.application.name=spring-boot-bulking-seata-account
server.port=8081
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_seata_1?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=111111
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath*:mapper/*Mapper.xml
seata.tx-service-group=my_test_tx_group
seata.service.grouplist=127.0.0.1:8091
logging.level.io.seata=info
logging.level.io.seata.samples.account.persistence.AccountMapper=debug
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
BusinessController提供了两个API入口,模拟下单成功、下单异常回滚
@GlobalTransactional
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
LOGGER.info("purchase begin ... , xid: " + RootContext.getXID());
// 扣减库存
storageClient.deduct(commodityCode, orderCount);
// 创建订单
orderClient.create(userId, commodityCode, orderCount);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
方法上添加@GlobalTransactional,描述启动全局性事务
以扣减库存为例,我们使用Spring框架的RestTemplate,通过Http接口访问远程服务,跨系统如何传递事务标识 XID?
@Component
public class StorageClient {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private static String storageURL = "http://127.0.0.1:8083/api/storage/deduct?commodityCode=%s&count=%s";
public void deduct(String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
System.out.println("invoke storage, xid: " + RootContext.getXID());
String url = String.format(storageURL, commodityCode, orderCount);
try {
ResponseEntity<String> result = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class);
System.out.println("[StorageClient] invoke,result=" + result.getBody());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("deduct url {} ,error:", url, e);
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
我们重写了ClientHttpRequestInterceptor拦截器,并注入到RestTemplate实例中。每次发送Http请求时,从ThreadLocal取到XID写入Header,然后再将请求发送给目标端。
@Component
public class RestTemplateInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest httpRequest, byte[] bytes, ClientHttpRequestExecution clientHttpRequestExecution) throws IOException {
HttpRequestWrapper requestWrapper = new HttpRequestWrapper(httpRequest);
String xid = RootContext.getXID();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(xid)) {
requestWrapper.getHeaders().add(RootContext.KEY_XID, xid);
}
return clientHttpRequestExecution.execute(requestWrapper, bytes);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Case 测试
Seata事务无论成功或者回滚,都会物理删除undo_log表里的记录,为了验证中间过程,我们在下游Order系统里的com.weiguanjishu.service.OrderService#create设置个断点,临时中断请求,然后查看各个表的数据变化
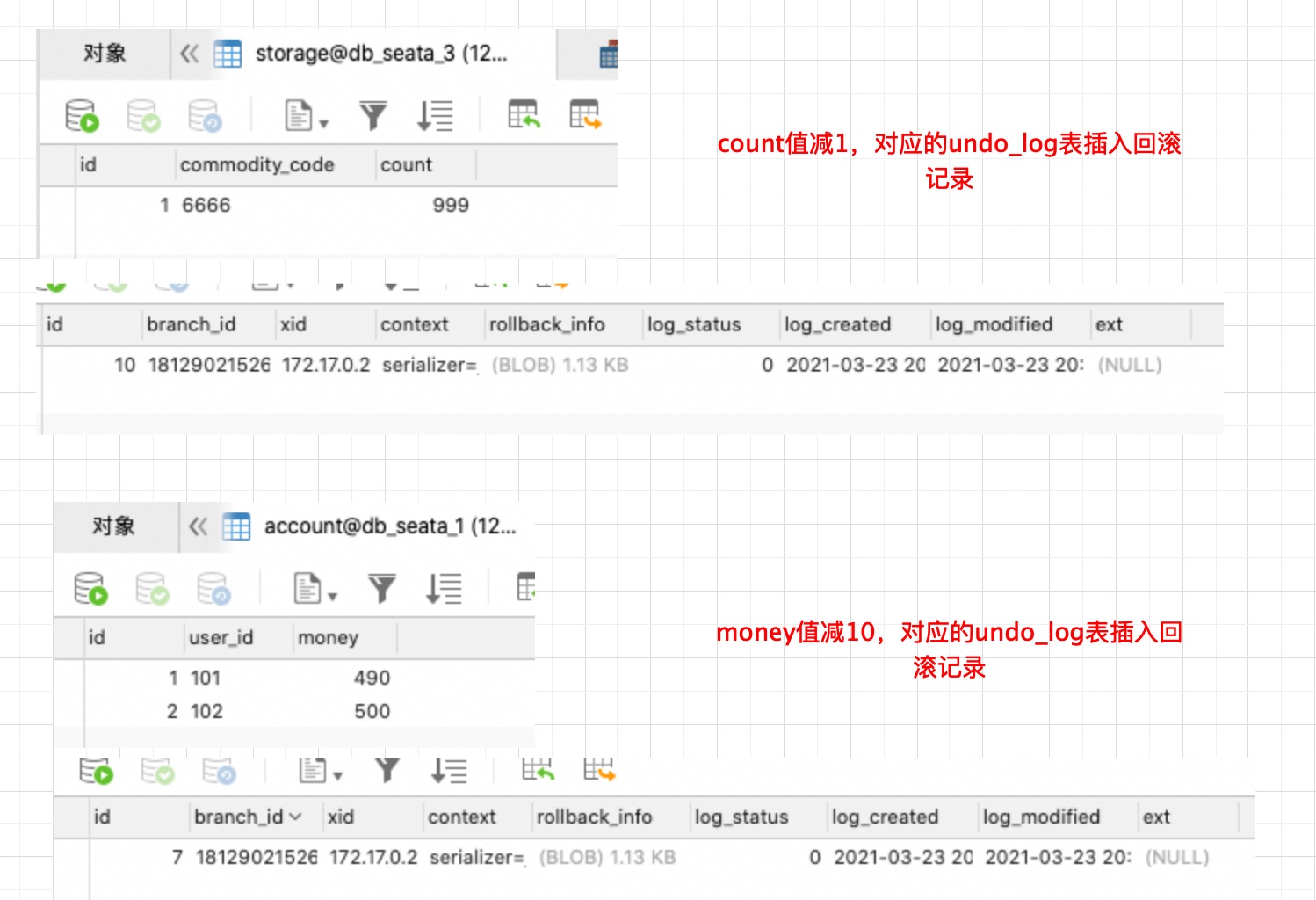
然后将断点放开,请求处理成功,再来看下各表的数据情况
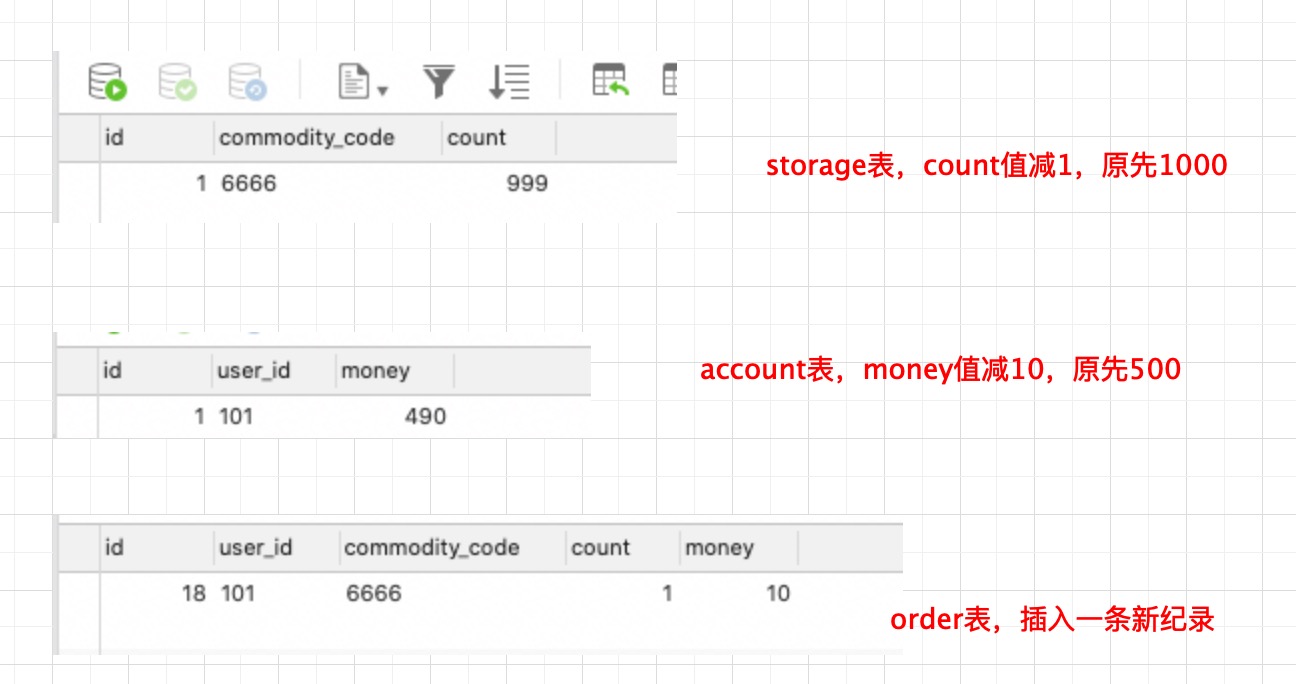
写在最后
Seata 与其它分布式事务最大的区别在于,它在第一提交阶段就已经将各个分支事务操作 commit 了。Seata 认为在一个正常的业务下,各个服务提交事务的大概率是成功的,这种事务提交操作可以节约两个阶段持有锁的时间,从而提高整体的执行效率。
# 项目源码
https://github.com/aalansehaiyang/spring-boot-bulking
子模块:
spring-boot-bulking-seata-business
spring-boot-bulking-seata-storage
spring-boot-bulking-seata-order
spring-boot-bulking-seata-account
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 资料
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9aZIGLJx7W9b51QA91fGLw
- https://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/overview/what-is-seata.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/hosaos/article/details/89136666
- http://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/overview/what-is-seata.html
